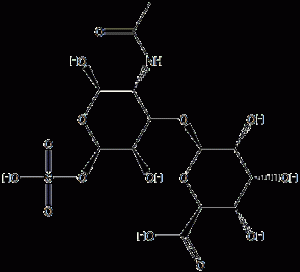
Chondroitin sulfate alang sa pagtambal sa sakit sa coronary heart, arthritis ug pag-ayo sa mga corneal samad sa kaputli 98%
Detalye sa Produkto
| Ngalan | Sulfate sa Chondroitin |
| CAS NUMBER | 9007-28-7 |
| Molecular nga pormula | C13h21no15s |
| Gibug-aton sa molekula | 463.36854 |
| Numero sa Einecs | 232-696-9 |
| Sakit sa Tubig | Matunaw sa tubig |
| Kalig-on | 98% |
| Tipiganan | Pagtipig sa regular nga temperatura |
| Porma | Pulbos |
| Bulok | Puti nga wala'y puti |
| Pagputos | PE Bag + Aluminum Bag |
Mga sinehero
Poly-1 (2/3) -n-Actyl-2-amino-2-o-beta-D-glucocopyranurosyl-4- galactosyl-d-galactose; chondroitinPoly sulfate; Mga sulfate sa Chondroitin; Chondroiti Nsulfuricacid; Mga asido nga Chondroitin Aids; chonsurid; CSO; (5ξ) -2- (Carboxyamino) -2-deoxy-3-O-O-glucopyranuron
Epekto sa pharmacological
Hulagway
Ang Chidroitinsulfate (CS) usa ka acidic mucopolysaccharide nga nakuha ug gihinloan gikan sa tisyu sa hayop nga carilage. Chondroitin sulfate has different structures such as A, C, D, E, H and K. Chondroitin sulfate in nature is mostly found in animal cartilage, throat bone, nasal bone (41% in pigs), bovine, horse septum and trachea (containing 36% to 39%), other tissues such as leg bones, ligaments, skin, cornea, etc. are also contained. Ang sulud sa cartilage sa isda dato kaayo, sama sa 50% hangtod 60% sa bukog sa iho, ug gamay ra sa nagkadugtong nga tisyu.
Alang sa Coronary Atheroscleric nga sakit, dugang nga mga lipid sa dugo ug kolesterol, arteriosloLClerosis, angina Pectoris, Myocardial Ischemction, uban pa sa mga pasyente nga adunay sakit sa coronary infent.
Aksyon sa Pharmacological
Ang Rapamycin (Rapa) adunay parehas nga mga epekto sa FK506. Sa daghang mga klinikal nga mga pagsulay, ang mga epekto niini nakit-an nga nagdepende sa dosis ug pag-usab, ug ang Rapa sa mga dosis sa terapyutik wala pa makit-an nga adunay gubot nga hyperplasia. Ang mga nag-unang makahilo ug mga epekto naglakip sa: sakit sa ulo, kasukaon, pagkalipong, nosebleeds, ug hiniusa nga kasakit. Laboratory abnormalities include: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, low hemoglobin, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, elevated liver enzymes (SGOT, SGPT), elevated lactate dehydrogenase, hypokalemia, Hypomagnesemia, etc. Eyelid edema was recently Gi-report sa administrasyong Rapa, ug ang hinungdan sa lebel sa ubos nga plasma nga lebel sa Phosphate gihunahuna nga dugay nga pagpagawas sa phosphate gikan sa tanum nga kidunosuppressive nga therapy. Sama sa uban nga mga immunosuppressant, adunay dugang nga higayon ang pag-uswag sa Rapa sa impeksyon, nga adunay usa ka gitaho nga hilig sa pagdugang sa pneumonia, apan ang panghinabo sa ubang mga oportunidad nga impeksyon dili lahi sa CSA.
Mga epekto sa toxicological
Ang Chondroitin sulfate sa kadaghanan naglungtad sa tisyu sa tawo ug hayop. Ang pag-andam sa medisina nag-una nga adunay duha ka isomer sa Chondroitin sulfate a ug chondroitin sulfate c, ug ang sulud sa condroitin sulfate sa lainlaing mga lahi sa lainlaing lahi ug edad. Ang mga epekto sa pharmacological mao ang mga musunud: Ang Sulfate ni Chontroitin mahimong makawagtang sa mga lipid sa dugo, kuhaa ang mga kolesterol sa mga ugat sa mga lipid ug fatty acid sa mga selyula. Ang sulay sa Chondroitin mahimong epektibo nga makapugong ug pagtratar sa sakit sa kasingkasing sa coronary. Kini adunay anti-atherosclerosis ug anti-atherogenic nga mga epekto sa pormasyon sa pagporma sa plake sa mga modelo nga eksperimento arteriosclerosis; Gipataas ang mga sanga sa coronary o collateral nga sirkulasyon sa atherosclerosis, ug mapadali ang eksperimento nga coronary arteriosclerosis o embolism. Pag-ayo, pagbag-o ug pag-ayo sa myocardial necrosis o pagkabulok. It can increase the biosynthesis of cell messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and has the effect of promoting cell metabolism. Ubos nga kalihokan sa anticoagulant. Ang Sulfate sa Chondroitin adunay usa ka kasarangan nga anticoagulant nga epekto, ug ang matag 1 mg sa Chondroitin sulfate a katumbas sa kalihokan nga anticoagulant nga 0.45U sa heparin. Kini nga kalihokan nga anticoagulant wala magdepende sa Anthrombin III nga ipatugtog ang papel niini, mahimo kini nga kalihokan sa Anticoagulant pinaagi sa sistema sa Fibrinogen. Ang Sulfate ni Chondroitin adunay usab anti-inflammatory, gipadali nga pag-ayo sa samad ug anti-tumor.